步骤4:使用常用nGQL(CRUD命令)Graph
本文介绍NebulaGraph查询语言的基础语法,包括用于Schema创建和常用增删改查操作的语句。
如需了解更多语句的用法,参见Graph。
图空间和SchemaGraph
一个NebulaGraph实例由一个或多个图空间组成。每个图空间都是物理隔离的,用户可以在同一个实例中使用不同的图空间存储不同的数据集。
为了在图空间中插入数据,需要为图数据库定义一个Schema。NebulaGraph的Schema是由如下几部分组成。
| 组成部分 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 点(Vertex) | 表示现实世界中的实体。一个点可以有一个或多个标签。 |
| 标签(Tag) | 点的类型,定义了一组描述点类型的属性。 |
| 边(Edge) | 表示两个点之间有方向的关系。 |
| 边类型(Edge type) | 边的类型,定义了一组描述边的类型的属性。 |
更多信息,请参见Graph。
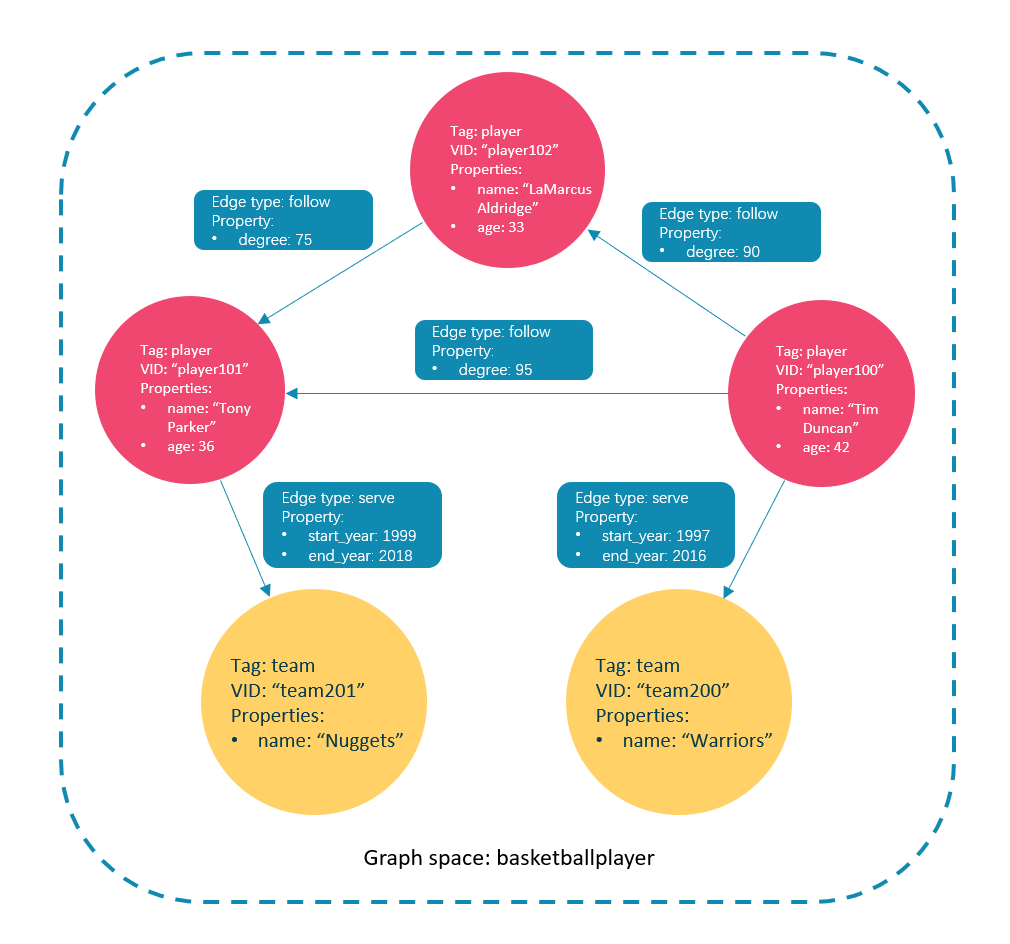
本文将使用下图的数据集演示基础操作的语法。
检查NebulaGraph集群的机器状态Graph
Note
首先建议检查机器状态,确保所有的Storage服务连接到了Meta服务。执行命令SHOW HOSTS查看机器状态。
nebula> SHOW HOSTS;
+-------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+----------------------+------------------------+
| Host | Port | Status | Leader count | Leader distribution | Partition distribution |
+-------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+----------------------+------------------------+
| "storaged0" | 9779 | "ONLINE" | 0 | "No valid partition" | "No valid partition" |
+-------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+----------------------+------------------------+
| "storaged1" | 9779 | "ONLINE" | 0 | "No valid partition" | "No valid partition" |
+-------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+----------------------+------------------------+
| "storaged2" | 9779 | "ONLINE" | 0 | "No valid partition" | "No valid partition" |
+-------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+----------------------+------------------------+
| "Total" | __EMPTY__ | __EMPTY__ | 0 | __EMPTY__ | __EMPTY__ |
+-------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+----------------------+------------------------+
Got 4 rows (time spent 1061/2251 us)
在返回结果中,查看Status列,可以看到所有Storage服务都在线。
异步实现创建和修改Graph
Caution
NebulaGraph中执行如下创建和修改操作,是异步实现的。要在下一个心跳周期之后才能生效;否则访问会报错。
CREATE SPACECREATE TAGCREATE EDGEALTER TAGALTER EDGECREATE TAG INDEXCREATE EDGE INDEX
Note
默认心跳周期是10秒。修改心跳周期参数heartbeat_interval_secs,请参见Graph。
为确保数据同步,后续操作能顺利进行,可采取以下方法之一:
- 执行
SHOW或DESCRIBE命令检查相应对象的状态,确保创建或修改已完成。如果没有完成,请等待几秒重试。
- 等待2个心跳周期(20秒)。
创建和选择图空间Graph
nGQL语法Graph
- 创建图空间
CREATE SPACE [IF NOT EXISTS] <graph_space_name> ( [partition_num = <partition_number>,] [replica_factor = <replica_number>,] vid_type = {FIXED_STRING(<N>) | INT64} ) [COMMENT = '<comment>'];参数详情请参见Graph。
- 列出创建成功的图空间
nebula> SHOW SPACES;
- 选择数据库
USE <graph_space_name>;
示例Graph
-
执行如下语句创建名为
basketballplayer的图空间。nebula> CREATE SPACE basketballplayer(partition_num=15, replica_factor=1, vid_type=fixed_string(30)); Execution succeeded (time spent 2817/3280 us) -
执行命令
SHOW HOSTS检查分片的分布情况,确保平衡分布。nebula> SHOW HOSTS; +-------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+----------------------------------+------------------------+ | Host | Port | Status | Leader count | Leader distribution | Partition distribution | +-------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+----------------------------------+------------------------+ | "storaged0" | 9779 | "ONLINE" | 5 | "basketballplayer:5" | "basketballplayer:5" | +-------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+----------------------------------+------------------------+ | "storaged1" | 9779 | "ONLINE" | 5 | "basketballplayer:5" | "basketballplayer:5" | +-------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+----------------------------------+------------------------+ | "storaged2" | 9779 | "ONLINE" | 5 | "basketballplayer:5" | "basketballplayer:5" | +-------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+----------------------------------+------------------------+ | "Total" | | | 15 | "basketballplayer:15" | "basketballplayer:15" | +-------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+----------------------------------+------------------------+ Got 4 rows (time spent 1633/2867 us)如果Leader distribution分布不均匀,请执行命令
BALANCE LEADER重新分配。更多信息,请参见Graph。 -
选择图空间
basketballplayer。nebula[(none)]> USE basketballplayer; Execution succeeded (time spent 1229/2318 us)用户可以执行命令
SHOW SPACES查看创建的图空间。nebula> SHOW SPACES; +--------------------+ | Name | +--------------------+ | "basketballplayer" | +--------------------+ Got 1 rows (time spent 977/2000 us)
创建Tag和Edge typeGraph
nGQL语法Graph
CREATE {TAG | EDGE} {<tag_name> | <edge_type>}(<property_name> <data_type>
[, <property_name> <data_type> ...])
[COMMENT = '<comment>'];
参数详情请参见Graph。
示例Graph
创建Tag:player和team,以及Edge type:follow和serve。说明如下表。
| 名称 | 类型 | 属性 |
|---|---|---|
| player | Tag | name (string), age (int) |
| team | Tag | name (string) |
| follow | Edge type | degree (int) |
| serve | Edge type | start_year (int), end_year (int) |
nebula> CREATE TAG player(name string, age int);
Execution succeeded (time spent 20708/22071 us)
nebula> CREATE TAG team(name string);
Execution succeeded (time spent 5643/6810 us)
nebula> CREATE EDGE follow(degree int);
Execution succeeded (time spent 12665/13934 us)
nebula> CREATE EDGE serve(start_year int, end_year int);
Execution succeeded (time spent 5858/6870 us)
插入点和边Graph
用户可以使用INSERT语句,基于现有的Tag插入点,或者基于现有的Edge type插入边。
nGQL语法Graph
- 插入点
INSERT VERTEX [IF NOT EXISTS] <tag_name> (<property_name>[, <property_name>...]) [, <tag_name> (<property_name>[, <property_name>...]), ...] {VALUES | VALUE} <vid>: (<property_value>[, <property_value>...]) [, <vid>: (<property_value>[, <property_value>...];VID是Vertex ID的缩写,VID在一个图空间中是唯一的。参数详情请参见Graph。
- 插入边
INSERT EDGE [IF NOT EXISTS] <edge_type> (<property_name>[, <property_name>...]) {VALUES | VALUE} <src_vid> -> <dst_vid>[@<rank>] : (<property_value>[, <property_value>...]) [, <src_vid> -> <dst_vid>[@<rank>] : (<property_name>[, <property_name>...]), ...];参数详情请参见Graph。
示例Graph
- 插入代表球员和球队的点。
nebula> INSERT VERTEX player(name, age) VALUES "player100":("Tim Duncan", 42); Execution succeeded (time spent 28196/30896 us) nebula> INSERT VERTEX player(name, age) VALUES "player101":("Tony Parker", 36); Execution succeeded (time spent 2708/3834 us) nebula> INSERT VERTEX player(name, age) VALUES "player102":("LaMarcus Aldridge", 33); Execution succeeded (time spent 1945/3294 us) nebula> INSERT VERTEX team(name) VALUES "team200":("Warriors"), "team201":("Nuggets"); Execution succeeded (time spent 2269/3310 us)
- 插入代表球员和球队之间关系的边。
nebula> INSERT EDGE follow(degree) VALUES "player100" -> "player101":(95); Execution succeeded (time spent 3362/4542 us) nebula> INSERT EDGE follow(degree) VALUES "player100" -> "player102":(90); Execution succeeded (time spent 2974/4274 us) nebula> INSERT EDGE follow(degree) VALUES "player102" -> "player101":(75); Execution succeeded (time spent 1891/3096 us) nebula> INSERT EDGE serve(start_year, end_year) VALUES "player100" -> "team200":(1997, 2016), "player101" -> "team201":(1999, 2018); Execution succeeded (time spent 6064/7104 us)
查询数据Graph
- Graph语句可以根据指定的条件遍历数据库。
GO语句从一个或多个点开始,沿着一条或多条边遍历,返回YIELD子句中指定的信息。
- Graph语句可以获得点或边的属性。
- Graph的,和
WHERE子句一起使用,查找符合特定条件的数据。
- Graph去匹配NebulaGraph中的数据模型,性能也还需要调优。
nGQL语法Graph
GOGO [[<M> TO] <N> STEPS ] FROM <vertex_list> OVER <edge_type_list> [REVERSELY] [BIDIRECT] [WHERE <expression> [AND | OR expression ...])] YIELD [DISTINCT] <return_list>;
-
FETCH-
查询Tag属性
FETCH PROP ON {<tag_name> | <tag_name_list> | *} <vid_list> [YIELD [DISTINCT] <return_list>];
-
查询边属性
FETCH PROP ON <edge_type> <src_vid> -> <dst_vid>[@<rank>] [, <src_vid> -> <dst_vid> ...] [YIELD [DISTINCT] <return_list>];
-
LOOKUPLOOKUP ON {<tag_name> | <edge_type>} WHERE <expression> [AND expression ...])] [YIELD <return_list>];
MATCHMATCH <pattern> [<WHERE clause>] RETURN <output>;
GO语句示例Graph
- 从VID为
player100的球员开始,沿着边follow找到连接的球员。nebula> GO FROM "player100" OVER follow; +-------------+ | follow._dst | +-------------+ | "player101" | +-------------+ | "player102" | +-------------+ Got 2 rows (time spent 12097/14220 us)
- 从VID为
player100的球员开始,沿着边follow查找年龄大于或等于35岁的球员,并返回他们的姓名和年龄,同时重命名对应的列。nebula> GO FROM "player100" OVER follow WHERE $$.player.age >= 35 \ YIELD $$.player.name AS Teammate, $$.player.age AS Age; +---------------+-----+ | Teammate | Age | +---------------+-----+ | "Tony Parker" | 36 | +---------------+-----+ Got 1 rows (time spent 8206/9335 us)子句/符号 说明 YIELD指定该查询需要返回的值或结果。 $$表示边的终点。 \表示换行继续输入。
-
从VID为
player100的球员开始,沿着边follow查找连接的球员,然后检索这些球员的球队。为了合并这两个查询请求,可以使用管道符或临时变量。-
使用管道符
nebula> GO FROM "player100" OVER follow YIELD follow._dst AS id | \ GO FROM $-.id OVER serve YIELD $$.team.name AS Team, \ $^.player.name AS Player; +-----------+---------------+ | Team | Player | +-----------+---------------+ | "Nuggets" | "Tony Parker" | +-----------+---------------+ Got 1 rows (time spent 5055/8203 us)子句/符号 说明 $^表示边的起点。 |组合多个查询的管道符,将前一个查询的结果集用于后一个查询。 $-表示管道符前面的查询输出的结果集。
-
使用临时变量
Note
当复合语句作为一个整体提交给服务器时,其中的临时变量会在语句结束时被释放。
nebula> $var = GO FROM "player100" OVER follow YIELD follow._dst AS id; \ GO FROM $var.id OVER serve YIELD $$.team.name AS Team, \ $^.player.name AS Player; +---------+-------------+ | Team | Player | +---------+-------------+ | Nuggets | Tony Parker | +---------+-------------+ Got 1 rows (time spent 3103/3711 us)
-
FETCH语句示例Graph
查询VID为player100的球员的属性。
nebula> FETCH PROP ON player "player100";
+----------------------------------------------------+
| vertices_ |
+----------------------------------------------------+
| ("player100" :player{age: 42, name: "Tim Duncan"}) |
+----------------------------------------------------+
Got 1 rows (time spent 2006/2406 us)
Note
LOOKUP和MATCH的示例在下文的Graph部分查看。
修改点和边Graph
用户可以使用UPDATE语句或UPSERT语句修改现有数据。
UPSERT是UPDATE和INSERT的结合体。当使用UPSERT更新一个点或边,如果它不存在,数据库会自动插入一个新的点或边。
Note
每个 partition 内部,UPSERT 操作是一个串行操作,所以执行速度比执行 INSERT 或 UPDATE 慢很多。其仅在多个 partition 之间有并发。
nGQL语法Graph
UPDATE点UPDATE VERTEX <vid> SET <properties to be updated> [WHEN <condition>] [YIELD <columns>];
UPDATE边UPDATE EDGE <source vid> -> <destination vid> [@rank] OF <edge_type> SET <properties to be updated> [WHEN <condition>] [YIELD <columns to be output>];
UPSERT点或边UPSERT {VERTEX <vid> | EDGE <edge_type>} SET <update_columns> [WHEN <condition>] [YIELD <columns>];
示例Graph
- 用
UPDATE修改VID为player100的球员的name属性,然后用FETCH语句检查结果。nebula> UPDATE VERTEX "player100" SET player.name = "Tim"; Execution succeeded (time spent 3483/3914 us) nebula> FETCH PROP ON player "player100"; +---------------------------------------------+ | vertices_ | +---------------------------------------------+ | ("player100" :player{age: 42, name: "Tim"}) | +---------------------------------------------+ Got 1 rows (time spent 2463/3042 us)
- 用
UPDATE修改某条边的degree属性,然后用FETCH检查结果。nebula> UPDATE EDGE "player100" -> "player101" OF follow SET degree = 96; Execution succeeded (time spent 3932/4432 us) nebula> FETCH PROP ON follow "player100" -> "player101"; +----------------------------------------------------+ | edges_ | +----------------------------------------------------+ | [:follow "player100"->"player101" @0 {degree: 96}] | +----------------------------------------------------+ Got 1 rows (time spent 2205/2800 us)
- 用
UPSERT插入一个VID为player111的点。nebula> INSERT VERTEX player(name, age) VALUES "player111":("Ben Simmons", 22); Execution succeeded (time spent 2115/2900 us) Wed, 21 Oct 2020 11:11:50 UTC nebula> UPSERT VERTEX "player111" SET player.name = "Dwight Howard", player.age = $^.player.age + 11 \ WHEN $^.player.name == "Ben Simmons" AND $^.player.age > 20 \ YIELD $^.player.name AS Name, $^.player.age AS Age; +---------------+-----+ | Name | Age | +---------------+-----+ | Dwight Howard | 33 | +---------------+-----+ Got 1 rows (time spent 1815/2329 us)
删除点和边Graph
nGQL语法Graph
- 删除点
DELETE VERTEX <vid1>[, <vid2>...]
- 删除边
DELETE EDGE <edge_type> <src_vid> -> <dst_vid>[@<rank>] [, <src_vid> -> <dst_vid>...]
示例Graph
- 删除点
nebula> DELETE VERTEX "team1", "team2"; Execution succeeded (time spent 4337/4782 us)
- 删除边
nebula> DELETE EDGE follow "team1" -> "team2"; Execution succeeded (time spent 3700/4101 us)
索引Graph
用户可以通过Graph语句为Tag和Edge type增加索引。
使用索引必读
MATCH和LOOKUP语句的执行都依赖索引,但是索引会导致写性能大幅降低(降低90%甚至更多)。请不要随意在生产环境中使用索引,除非很清楚使用索引对业务的影响。
必须为“已写入但未构建索引”的数据重建索引,否则无法在MATCH和LOOKUP语句中返回这些数据。参见Graph。
nGQL语法Graph
- 创建索引
CREATE {TAG | EDGE} INDEX [IF NOT EXISTS] <index_name> ON {<tag_name> | <edge_name>} ([<prop_name_list>]) [COMMENT = '<comment>'];
- 重建索引
REBUILD {TAG | EDGE} INDEX <index_name>;
示例Graph
为Tagplayer的属性name创建索引,并且重建索引。
nebula> CREATE TAG INDEX player_index_0 on player(name(20));
nebula> REBUILD TAG INDEX player_index_0;
Note
为没有指定长度的变量属性创建索引时,需要指定索引长度。在utf-8编码中,一个中文字符占3字节,请根据变量属性长度设置合适的索引长度。例如10个中文字符,索引长度需要为30。详情请参见Graph。
基于索引的LOOKUP和MATCH示例Graph
确保LOOKUP或MATCH有一个索引可用。如果没有,请先创建索引。
找到Tag为player的点的信息,它的name属性值为Tony Parker。
// 为name属性创建索引player_name_0。
nebula> CREATE TAG INDEX player_name_0 on player(name(10));
Execution succeeded (time spent 3465/4150 us)
// 重建索引确保能对已存在数据生效。
nebula> REBUILD TAG INDEX player_name_0
+------------+
| New Job Id |
+------------+
| 31 |
+------------+
Got 1 rows (time spent 2379/3033 us)
// 使用LOOKUP语句检索点的属性。
nebula> LOOKUP ON player WHERE player.name == "Tony Parker" \
YIELD player.name, player.age;
+-------------+---------------+------------+
| VertexID | player.name | player.age |
+-------------+---------------+------------+
| "player101" | "Tony Parker" | 36 |
+-------------+---------------+------------+
// 使用MATCH语句检索点的属性。
nebula> MATCH (v:player{name:"Tony Parker"}) RETURN v;
+-----------------------------------------------------+
| v |
+-----------------------------------------------------+
| ("player101" :player{age: 36, name: "Tony Parker"}) |
+-----------------------------------------------------+
Got 1 rows (time spent 5132/6246 us)