Gremlin 和 nGQL 对比Graph
Gremlin 介绍Graph
Graph 是 Apache ThinkerPop 框架下的图遍历语言。Gremlin 可以是声明性的也可以是命令性的。虽然 Gremlin 是基于 Groovy 的,但具有许多语言变体,允许开发人员以 Java、JavaScript、Python、Scala、Clojure 和 Groovy 等许多现代编程语言原生编写 Gremlin 查询。
nGQL 介绍Graph
NebulaGraph 的查询语言为 Graph, 是一种类 SQL 的声明型的文本查询语言。相比 SQL,nGQL 具有如下特点:
- 类 SQL,易学易用
- 可扩展
- 关键词大小写不敏感
- 支持图遍历
- 支持模式匹配
- 支持聚合运算
- 支持图计算
- 支持分布式事务(开发中)
- 无嵌入支持组合语句,易于阅读
基本概念对比Graph
| 名称 | Gremlin | nGQL |
|---|---|---|
| vertex, node | vertex | vertex |
| edge, relationship | edge | edge |
| vertex type | label | tag |
| edge type | label | edge type |
| vertex id | vid | vid |
| edge id | eid | 无 |
Gremlin 和 nGQL 均使用唯一标识符标记顶点和边。在 NebulaGraph 中,用户可以使用指定标识符、哈希或 uuid 函数自动生成标识符。
图基本操作Graph
| 名称 | Gremlin | nGQL |
|---|---|---|
| 新建图空间 | g = TinkerGraph.open().traversal() | CREATE SPACE gods |
| 查看点类型 | g.V().label() | SHOW TAGS |
| 插入指定类型点 | g.addV(String vertexLabel).property() | INSERT VERTEX <tag_name> (prop_name_list) VALUES <vid>:(prop_value_list) |
| 插入指定类型边 | g.addE(String edgeLabel).from(v1).to(v2).property() | INSERT EDGE <edge_name> ( <prop_name_list> ) VALUES <src_vid> -> <dst_vid>: ( <prop_value_list> ) |
| 删除点 | g.V(<vid>).drop() |
DELETE VERTEX <vid> |
| 删除边 | g.E(<vid>).outE(<type>).where(otherV().is(<vid>))drop() |
DELETE EDGE <edge_type> <src_vid> -> <dst_vid> |
| 更新点属性 | g.V(<vid>).property() |
UPDATE VERTEX <vid> SET <update_columns> |
| 查看指定点 | g.V(<vid>) |
FETCH PROP ON <tag_name> <vid> |
| 查看指定边 | g.E(<src_vid> >> <dst_vid>) |
FETCH PROP ON <edge_name> <src_vid> -> <dst_vid> |
| 沿指定点查询指定边 | g.V(<vid>).outE( <edge>) |
GO FROM <vid> OVER <edge> |
| 沿指定点反向查询指定边 | g.V(<vid>).in( <edge>) |
GO FROM <vid> OVER <edge> REVERSELY |
| 沿指定点查询指定边 N 跳 | g.V(<vid>).repeat(out(<edge>)).times(N) |
GO N STEPS FROM <vid> OVER <edge> |
| 返回指定两点路径 | g.V(<vid>).repeat(out()).until(<vid>).path() |
FIND ALL PATH FROM <vid> TO <vid> OVER * |
示例查询Graph
本节中的示例使用了 Graph描述罗马万神话中诸神关系。
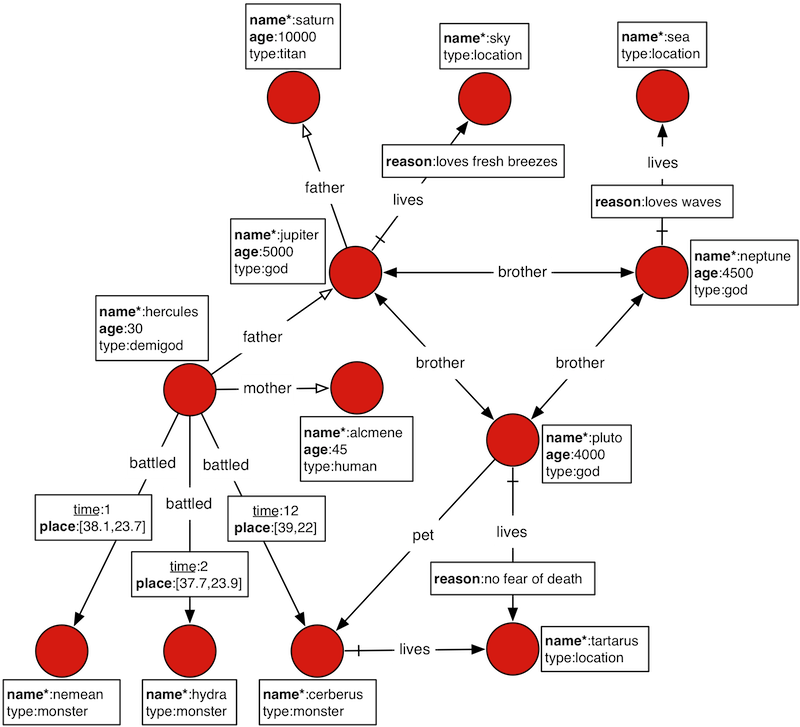
- 插入数据
# 插入点
nebula> INSERT VERTEX character(name, age, type) VALUES hash("saturn"):("saturn", 10000, "titan"), hash("jupiter"):("jupiter", 5000, "god");
gremlin> saturn = g.addV("character").property(T.id, 1).property('name', 'saturn').property('age', 10000).property('type', 'titan').next();
==>v[1]
gremlin> jupiter = g.addV("character").property(T.id, 2).property('name', 'jupiter').property('age', 5000).property('type', 'god').next();
==>v[2]
gremlin> prometheus = g.addV("character").property(T.id, 31).property('name', 'prometheus').property('age', 1000).property('type', 'god').next();
==>v[31]
gremlin> jesus = g.addV("character").property(T.id, 32).property('name', 'jesus').property('age', 5000).property('type', 'god').next();
==>v[32]
# 插入边
nebula> INSERT EDGE father() VALUES hash("jupiter")->hash("saturn"):();
gremlin> g.addE("father").from(jupiter).to(saturn).property(T.id, 13);
==>e[13][2-father->1]
- 删除数据
nebula> DELETE VERTEX hash("prometheus");
gremlin> g.V(prometheus).drop();
- 更新数据
nebula> UPDATE VERTEX hash("jesus") SET character.type = 'titan';
gremlin> g.V(jesus).property('age', 6000);
- 查看数据
nebula> FETCH PROP ON character hash("saturn");
===================================================
| character.name | character.age | character.type |
===================================================
| saturn | 10000 | titan |
---------------------------------------------------
gremlin> g.V(saturn).valueMap();
==>[name:[saturn],type:[titan],age:[10000]]
- 查询 hercules 的祖父
nebula> LOOKUP ON character WHERE character.name == 'hercules' | \
-> GO 2 STEPS FROM $-.VertexID OVER father YIELD $$.character.name;
=====================
| $$.character.name |
=====================
| saturn |
---------------------
gremlin> g.V().hasLabel('character').has('name','hercules').out('father').out('father').values('name');
==>saturn
- 查询 hercules 的父亲
nebula> LOOKUP ON character WHERE character.name == 'hercules' | \
-> GO FROM $-.VertexID OVER father YIELD $$.character.name;
=====================
| $$.character.name |
=====================
| jupiter |
---------------------
gremlin> g.V().hasLabel('character').has('name','hercules').out('father').values('name');
==>jupiter
- 查询年龄大于 100 的人物
nebula> LOOKUP ON character WHERE character.age > 100 YIELD character.name, character.age;
=========================================================
| VertexID | character.name | character.age |
=========================================================
| 6761447489613431910 | pluto | 4000 |
---------------------------------------------------------
| -5860788569139907963 | neptune | 4500 |
---------------------------------------------------------
| 4863977009196259577 | jupiter | 5000 |
---------------------------------------------------------
| -4316810810681305233 | saturn | 10000 |
---------------------------------------------------------
gremlin> g.V().hasLabel('character').has('age',gt(100)).values('name');
==>saturn
==>jupiter
==>neptune
==>pluto
- 查询和 pluto 一起居住的人物
nebula> GO FROM hash("pluto") OVER lives YIELD lives._dst AS place | \
GO FROM $-.place OVER lives REVERSELY YIELD $$.character.name AS cohabitants;
===============
| cohabitants |
===============
| pluto |
---------------
| cerberus |
---------------
gremlin> g.V(pluto).out('lives').in('lives').values('name');
==>pluto
==>cerberus
- 从一起居住的人物中排除 pluto 本人
nebula> GO FROM hash("pluto") OVER lives YIELD lives._dst AS place | GO FROM $-.place OVER lives REVERSELY WHERE \
$$.character.name != "pluto" YIELD $$.character.name AS cohabitants;
===============
| cohabitants |
===============
| cerberus |
---------------
gremlin> g.V(pluto).out('lives').in('lives').where(is(neq(pluto))).values('name');
==>cerberus
- Pluto 的兄弟们
# where do pluto's brothers live?
nebula> GO FROM hash("pluto") OVER brother YIELD brother._dst AS brother | \
GO FROM $-.brother OVER lives YIELD $$.location.name;
====================
| $$.location.name |
====================
| sky |
--------------------
| sea |
--------------------
gremlin> g.V(pluto).out('brother').out('lives').values('name');
==>sky
==>sea
# which brother lives in which place?
nebula> GO FROM hash("pluto") OVER brother YIELD brother._dst AS god | \
GO FROM $-.god OVER lives YIELD $^.character.name AS Brother, $$.location.name AS Habitations;
=========================
| Brother | Habitations |
=========================
| jupiter | sky |
-------------------------
| neptune | sea |
-------------------------
gremlin> g.V(pluto).out('brother').as('god').out('lives').as('place').select('god','place').by('name');
==>[god:jupiter, place:sky]
==>[god:neptune, place:sea]
高级查询Graph
图探索Graph
# gremlin 版本
gremlin> Gremlin.version();
==>3.3.5
# 返回所有点
gremlin> g.V();
==>v[1]
==>v[2]
...
nebula> # Coming soon
# 统计点数
gremlin> g.V().count();
==>12
nebula> # Coming soon
# 按照点边类型统计点边个数
gremlin> g.V().groupCount().by(label);
==>[character:9,location:3]
gremlin> g.E().groupCount().by(label);
==>[mother:1,lives:5,father:2,brother:6,battled:3,pet:1]
nebula> # Coming soon
# 返回所有边
gremlin> g.E();
==>e[13][2-father->1]
==>e[14][2-lives->3]
...
nebula> # Coming soon
# 查询所有点类型
gremlin> g.V().label().dedup();
==>character
==>location
nebula> SHOW TAGS;
==================
| ID | Name |
==================
| 15 | character |
------------------
| 16 | location |
------------------
# 查询所有边类型
gremlin> g.E().label().dedup();
==>father
==>lives
...
nebula> SHOW EDGES;
================
| ID | Name |
================
| 17 | father |
----------------
| 18 | brother |
----------------
...
# 查询所有顶点的属性
gremlin> g.V().valueMap();
==>[name:[saturn],type:[titan],age:[10000]]
==>[name:[jupiter],type:[god],age:[5000]]
...
nebula> # Coming soon
# 查询 character 顶点属性
gremlin> g.V().hasLabel('character').valueMap();
==>[name:[saturn],type:[titan],age:[10000]]
==>[name:[jupiter],type:[god],age:[5000]]
...
边的遍历Graph
| 名称 | Gremlin | nGQL |
|---|---|---|
| 指定点沿指定边的出顶点 | out(\ | GO FROM \ |
| 指定点沿指定边的入顶点 | in(\ | GO FROM \ |
| 指定点沿指定边的双向顶点 | both(\ | GO FROM \ |
# 访问某个顶点沿某条边的 OUT 方向邻接点
gremlin> g.V(jupiter).out('brother');
==>v[8]
==>v[5]
nebula> GO FROM hash("jupiter") OVER brother;
========================
| brother._dst |
========================
| 6761447489613431910 |
------------------------
| -5860788569139907963 |
------------------------
# 访问某个顶点沿某条边的 IN 方向邻接点
gremlin> g.V(jupiter).in('brother');
==>v[5]
==>v[8]
nebula> GO FROM hash("jupiter") OVER brother REVERSELY;
=======================
| brother._dst |
=======================
| 4863977009196259577 |
-----------------------
| 4863977009196259577 |
-----------------------
# 访问某个顶点沿某条边的双向邻接点
gremlin> g.V(jupiter).both('brother');
==>v[8]
==>v[5]
==>v[5]
==>v[8]
nebula> GO FROM hash("jupiter") OVER brother BIDIRECT;
=======================
| brother._dst |
=======================
| 6761447489613431910 |
------------------------
| -5860788569139907963|
| 4863977009196259577 |
-----------------------
| 4863977009196259577 |
-----------------------
# 2度 out 查询
gremlin> g.V(hercules).out('father').out('lives');
==>v[3]
nebula> GO FROM hash("hercules") OVER father YIELD father._dst AS id | \
GO FROM $-.id OVER lives;
========================
| lives._dst |
========================
| -1121386748834253737 |
------------------------
has 条件过滤Graph
| 名称 | Gremlin | nGQL |
|---|---|---|
| 通过 ID 来过滤顶点 | hasId(\ |
FETCH PROP ON \ |
| 通过 label 和属性的名字和值过滤顶点和边 | has(\ | LOOKUP \ |
# 查询 ID 为 saturn 的顶点
gremlin> g.V().hasId(saturn);
==>v[1]
nebula> FETCH PROP ON * hash("saturn");
==========================================================================
| VertexID | character.name | character.age | character.type |
==========================================================================
| -4316810810681305233 | saturn | 10000 | titan |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 查询 tag 为 character 且 name 属性值为 hercules 的顶点
gremlin> g.V().has('character','name','hercules').valueMap();
==>[name:[hercules],type:[demigod],age:[30]]
nebula> LOOKUP ON character WHERE character.name == 'hercules' YIELD character.name, character.age, character.type;
=========================================================================
| VertexID | character.name | character.age | character.type |
=========================================================================
| 5976696804486077889 | hercules | 30 | demigod |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
返回结果限制Graph
| 名称 | Gremlin | nGQL |
|---|---|---|
| 指定返回结果行数 | limit() | LIMIT |
| 获取后 n 个元素 | tail() | ORDER BY \ |
| 跳过前 n 个元素 | skip() | LIMIT \ |
# 查询前两个顶点
gremlin> g.V().has('character','name','hercules').out('battled').limit(2);
==>v[9]
==>v[10]
nebula> GO FROM hash('hercules') OVER battled | LIMIT 2;
=======================
| battled._dst |
=======================
| 530133512982221454 |
-----------------------
| -695163537569412701 |
-----------------------
# 查询最后一个顶点
gremlin> g.V().has('character','name','hercules').out('battled').values('name').tail(1);
==>cerberus
nebula> GO FROM hash('hercules') OVER battled YIELD $$.character.name AS name | ORDER BY name | LIMIT 1;
============
| name |
============
| cerberus |
------------
# 跳过第 1 个元素并返回一个元素
gremlin> g.V().has('character','name','hercules').out('battled').values('name').skip(1).limit(1);
==>hydra
nebula> GO FROM hash('hercules') OVER battled YIELD $$.character.name AS name | ORDER BY name | LIMIT 1,1;
=========
| name |
=========
| hydra |
---------
路径查询Graph
| 名称 | Gremlin | nGQL |
|---|---|---|
| 所有路径 | path() | FIND ALL PATH |
| 不包含环路 | simplePath() | \ |
| 只包含环路 | cyclicPath() | \ |
| 最短路径 | \ | FIND SHORTEST PATH |
注意: NebulaGraph 需要起始点和终点方可返回路径, Gremlin 仅需要起始点。
# pluto 顶点到与其有直接关联的出边顶点的路径
gremlin> g.V().hasLabel('character').has('name','pluto').out().path();
==>[v[8],v[12]]
==>[v[8],v[2]]
==>[v[8],v[5]]
==>[v[8],v[11]]
# 查询点 pluto 到点 jupiter 的最短路径
nebula> LOOKUP ON character WHERE character.name== "pluto" YIELD character.name AS name | \
FIND SHORTEST PATH FROM $-.VertexID TO hash("jupiter") OVER *;
============================================================
| _path_ |
============================================================
| 6761447489613431910 <brother,0> 4863977009196259577
------------------------------------------------------------
多度查询Graph
| 名称 | Gremlin | nGQL |
|---|---|---|
| 指定重复执行的语句 | repeat() | N STEPS |
| 指定重复执行的次数 | times() | N STEPS |
| 指定循环终止的条件 | until() | \ |
| 指定收集数据的条件 | emit() | \ |
# 查询点 pluto 出边邻点
gremlin> g.V().hasLabel('character').has('name','pluto').repeat(out()).times(1);
==>v[12]
==>v[2]
==>v[5]
==>v[11]
nebula> LOOKUP ON character WHERE character.name== "pluto" YIELD character.name AS name | \
GO FROM $-.VertexID OVER *;
================================================================================================================
| father._dst | brother._dst | lives._dst | mother._dst | pet._dst | battled._dst |
================================================================================================================
| 0 | -5860788569139907963 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | 4863977009196259577 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | 0 | -4331657707562925133 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4594048193862126013 | 0 |
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 查询顶点 hercules 到顶点 cerberus 之间的路径
# 循环的终止条件是遇到名称是 cerberus 的顶点
gremlin> g.V().hasLabel('character').has('name','hercules').repeat(out()).until(has('name', 'cerberus')).path();
==>[v[6],v[11]]
==>[v[6],v[2],v[8],v[11]]
==>[v[6],v[2],v[5],v[8],v[11]]
...
nebula> # Coming soon
# 查询点 hercules 的所有出边可到达点的路径
# 且终点必须是 character 类型的点
gremlin> g.V().hasLabel('character').has('name','hercules').repeat(out()).emit(hasLabel('character')).path();
==>[v[6],v[7]]
==>[v[6],v[2]]
==>[v[6],v[9]]
==>[v[6],v[10]]
...
nebula> # Coming soon
# 查询两顶点 pluto 和 saturn 之间的最短路径
# 且最大深度为 3
gremlin> g.V('pluto').repeat(out().simplePath()).until(hasId('saturn').and().loops().is(lte(3))).hasId('saturn').path();
nebula> FIND SHORTEST PATH FROM hash('pluto') TO hash('saturn') OVER * UPTO 3 STEPS;
=================================================================================================
| _path_ |
=================================================================================================
| 6761447489613431910 <brother,0> 4863977009196259577 <father,0> -4316810810681305233
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
查询结果排序Graph
| 名称 | Gremlin | nGQL |
|---|---|---|
| 升序排列 | order().by() | ORDER BY |
| 降序排列 | order().by(decr) | ORDER BY DESC |
| 随机排列 | order().by(shuffle) | \ |
# 查询 pluto 的兄弟并按照年龄降序排列
gremlin> g.V(pluto).out('brother').order().by('age', decr).valueMap();
==>[name:[jupiter],type:[god],age:[5000]]
==>[name:[neptune],type:[god],age:[4500]]
nebula> GO FROM hash('pluto') OVER brother YIELD $$.character.name AS Name, $$.character.age as Age | ORDER BY Age DESC;
==================
| Name | Age |
==================
| jupiter | 5000 |
------------------
| neptune | 4500 |
------------------
Group ByGraph
| 名称 | Gremlin | nGQL |
|---|---|---|
| 对结果集进行分组 | group().by() | GROUP BY |
| 去除相同元素 | dedup() | DISTINCT |
| 对结果集进行分组并统计 | groupCount() | GROUP BY COUNT |
注意: GROUP BY 函数只能与 YIELD 语句一起使用。
# 根据顶点类别进行分组并统计各个类别的数量
gremlin> g.V().group().by(label).by(count());
==>[character:9,location:3]
nebula> # Coming soon
# 查询点 jupiter 出边邻点,使用 name 分组并统计
gremlin> g.V(jupiter).out().group().by('name').by(count());
==>[sky:1,saturn:1,neptune:1,pluto:1]
nebula> GO FROM hash('jupiter') OVER * YIELD $$.character.name AS Name, $$.character.age as Age, $$.location.name | \
GROUP BY $-.Name YIELD $-.Name, COUNT(*);
======================
| $-.Name | COUNT(*) |
======================
| | 1 |
----------------------
| pluto | 1 |
----------------------
| saturn | 1 |
----------------------
| neptune | 1 |
----------------------
# 查找点 jupiter 出边到达的点并去重
gremlin> g.V(jupiter).out().hasLabel('character').dedup();
==>v[1]
==>v[8]
==>v[5]
nebula> GO FROM hash('jupiter') OVER * YIELD DISTINCT $$.character.name, $$.character.age, $$.location.name;
===========================================================
| $$.character.name | $$.character.age | $$.location.name |
===========================================================
| pluto | 4000 | |
-----------------------------------------------------------
| neptune | 4500 | |
-----------------------------------------------------------
| saturn | 10000 | |
-----------------------------------------------------------
| | 0 | sky |
-----------------------------------------------------------
where 条件过滤Graph
| 名称 | Gremlin | nGQL |
|---|---|---|
| where 条件过滤 | where() | WHERE |
过滤条件对比:
| 名称 | Gremlin | nGQL |
|---|---|---|
| 等于 | eq(object) | == |
| 不等于 | neq(object) | != |
| 小于 | lt(number) | < |
| 小于等于 | lte(number) | <= |
| 大于 | gt(number) | > |
| 大于等于 | gte(number) | >= |
| 判断值是否在指定的列表中 | within(objects…) | udf_is_in() |
gremlin> eq(2).test(3);
==>false
nebula> YIELD 3 == 2;
==========
| (3==2) |
==========
| false |
----------
gremlin> within('a','b','c').test('d');
==>false
nebula> YIELD udf_is_in('d', 'a', 'b', 'c');
======================
| udf_is_in(d,a,b,c) |
======================
| false |
----------------------
# 找出 pluto 和谁住并排队他本人
gremlin> g.V(pluto).out('lives').in('lives').where(is(neq(pluto))).values('name');
==>cerberus
nebula> GO FROM hash("pluto") OVER lives YIELD lives._dst AS place | GO FROM $-.place OVER lives REVERSELY WHERE \
$$.character.name != "pluto" YIELD $$.character.name AS cohabitants;
===============
| cohabitants |
===============
| cerberus |
---------------
逻辑运算Graph
| 名称 | Gremlin | nGQL |
|---|---|---|
| Is | is() | == |
| Not | not() | != |
| And | and() | AND |
| Or | or() | OR |
# 查询年龄大于 30 的人物
gremlin> g.V().values('age').is(gte(30));
==>10000
==>5000
==>4500
==>30
==>45
==>4000
nebula> LOOKUP ON character WHERE character.age >= 30 YIELD character.age;
========================================
| VertexID | character.age |
========================================
| -4316810810681305233 | 10000 |
---------------------------------------–
| 4863977009196259577 | 5000 |
---------------------------------------–
| -5860788569139907963 | 4500 |
---------------------------------------–
| 5976696804486077889 | 30 |
---------------------------------------–
| -6780323075177699500 | 45 |
---------------------------------------–
| 6761447489613431910 | 4000 |
---------------------------------------–
# 查询名称为 pluto 且年龄为 4000 的人物
gremlin> g.V().has('name','pluto').and().has('age',4000);
==>v[8]
nebula> LOOKUP ON character WHERE character.name == 'pluto' AND character.age == 4000;
=======================
| VertexID |
=======================
| 6761447489613431910 |
-----------------------
# 逻辑非的用法
gremlin> g.V().has('name','pluto').out('brother').not(values('name').is('neptune')).values('name');
==>jupiter
nebula> LOOKUP ON character WHERE character.name == 'pluto' YIELD character.name AS name | \
GO FROM $-.VertexID OVER brother WHERE $$.character.name != 'neptune' YIELD $$.character.name;
=====================
| $$.character.name |
=====================
| jupiter |
---------------------
统计运算Graph
| 名称 | Gremlin | nGQL |
|---|---|---|
| 求和 | sum() | SUM() |
| 最大值 | max() | MAX() |
| 最小值 | min() | MIN() |
| 平均值 | mean() | AVG() |
NebulaGraph 统计运算必须同
GROUP BY一起使用。
# 计算所有 character 的年龄的总和
gremlin> g.V().hasLabel('character').values('age').sum();
==>23595
nebula> # Coming soon
# 计算所有 character 的 brother 出边数的总和
gremlin> g.V().hasLabel('character').map(outE('brother').count()).sum();
==>6
nebula> # Coming soon
# 返回所有 character 的年龄中的最大值
gremlin> g.V().hasLabel('character').values('age').max();
==>10000
nebula> # Coming soon
路径选取与过滤Graph
# 从路径中选取第 1 步和第 3 步的结果作为最终结果
gremlin> g.V(pluto).as('a').out().as('b').out().as('c').select('a','c');
==>[a:v[8],c:v[3]]
==>[a:v[8],c:v[1]]
...
nebula> # Coming soon
# 通过 by() 指定选取的维度
gremlin> g.V(pluto).as('a').out().as('b').out().as('c').select('a','c').by('name');
==>[a:pluto,c:sky]
==>[a:pluto,c:saturn]
...
nebula> # Coming soon
# 从 map 中选择指定 key 的值
gremlin> g.V().valueMap().select('name').dedup();
==>[saturn]
==>[jupiter]
...
nebula> # Coming soon
分支Graph
# 查找所有类型为 'character' 的顶点
# name 属性为 'jupiter' 的顶点输出其 age 属性
# 否则输出顶点的 name 属性
gremlin> g.V().hasLabel('character').choose(values('name')).option('jupiter', values('age')).option(none, values('name'));
==>saturn
==>5000
==>neptune
...
# Lambda
gremlin> g.V().branch {it.get().value('name')}.option('jupiter', values('age')).option(none, values('name'));
==>saturn
==>5000
...
# Traversal
gremlin> g.V().branch(values('name')).option('jupiter', values('age')).option(none, values('name'));
==>saturn
==>5000
# Branch
gremlin> g.V().choose(has('name','jupiter'),values('age'),values('name'));
==>saturn
==>5000
# 基于 if then 进行分组
gremlin> g.V().hasLabel("character").groupCount().by(values("age").choose(
is(lt(40)),constant("young"),
choose(is(lt(4500)),
constant("old"),
constant("very old"))));
==>[young:4,old:2,very old:3]
NebulaGraph 尚无类似功能。
合并Graph
coalesce() 可以接受任意数量的遍历器(traversal),按顺序执行,并返回第一个能产生输出的遍历器的结果。
optional() 只能接受一个遍历器(traversal),如果该遍历器能产生一个结果,则返回该结果,否则返回调用 optionalStep 的元素本身。
union() 可以接受任意数量的遍历器,并能够将各个遍历器的输出合并到一起。
# 如果类型为 monster 则返回类型否则返回 'Not a monster'
gremlin> g.V(pluto).coalesce(has('type','monster').values('type'),constant("Not a monster"));
==>Not a monster
# 按优先级寻找到顶点 jupiter 的以下边和邻接点,找到一个就停止
# 1、brother 出边和邻接点
# 2、father 出边和邻接点
# 3、father 入边和邻接点
gremlin> g.V(jupiter).coalesce(outE('brother'), outE('father'), inE('father')).inV().path().by('name').by(label);
==>[jupiter,brother,pluto]
==>[jupiter,brother,neptune]
# 查找顶点 pluto 的 father 出顶点,如果没有就返回 pluto 自己
gremlin> g.V(pluto).optional(out('father')).valueMap();
==>[name:[pluto],type:[god],age:[4000]]
# 寻找顶点 pluto 的出 father 顶点,邻接 brother 顶点,并将结果合并,最后打印出路径
gremlin> g.V(pluto).union(out('father'),both('brother')).path();
==>[v[8],v[2]]
==>[v[8],v[5]]
NebulaGraph 尚无类似功能。
结果聚集与展开Graph
# 收集第 1 步的结果到集合 x 中
# 注意:不影响后续结果
gremlin> g.V(pluto).out().aggregate('x');
==>v[12]
==>v[2]
...
# 通过 by() 指定聚集的维度
gremlin> g.V(pluto).out().aggregate('x').by('name').cap('x');
==>[tartarus,jupiter,neptune,cerberus]
# 查询与 pluto 的两度 OUT 邻居
# 并收集这些到 x 集合里面
# 最终以 name 属性展示其邻居
gremlin> g.V(pluto).out().aggregate('x').out().aggregate('x').cap('x').unfold().values('name');
==>tartarus
==>tartarus
...
NebulaGraph 尚无类似功能。
模式匹配Graph
match() 语句为图查询提供了一种基于模式匹配的方式,以便用更具描述性的方式进行图查询。match()语句通过多个模式片段 traversal fragments 来进行模式匹配。这些 traversal fragments 中会定义一些变量,只有满足所有用变量表示的约束的对象才能够通过。
# 对每一个顶点,用以下模式去匹配,满足则生成一个 map<String, Object>,不满足则过滤掉
# 模式1:a 为沿 father 出边指向 jupiter 的顶点
# 模式2:b 对应当前顶点 jupiter
# 模式3:c 对应创建 jupiter 的 brother 年龄为 4000 的 顶点
gremlin> g.V().match(__.as('a').out('father').has('name', 'jupiter').as('b'), __.as('b').in('brother').has('age', 4000).as('c'));
==>[a:v[6],b:v[2],c:v[8]]
# match() 语句可以与 select() 语句配合使用,从 Map<String, Object> 中选取部分结果
gremlin> g.V().match(__.as('a').out('father').has('name', 'jupiter').as('b'), __.as('b').in('brother').has('age', 4000).as('c')).select('a', 'c').by('name');
==>[a:hercules,c:pluto]
# match() 语句可以与 where() 语句配合使用,过滤结果
gremlin> g.V().match(__.as('a').out('father').has('name', 'jupiter').as('b'), __.as('b').in('brother').has('age', 4000).as('c')).where('a', neq('c')).select('a', 'c').by('name');
==>[a:hercules,c:pluto]
随机过滤Graph
sample() 接受一个整数值,从前一步的遍历器中采样(随机)出最多指定数目的结果。
coin() 字面意思是抛硬币过滤,接受一个浮点值,该浮点值表示硬币出现正面的概率。
# 从所有顶点的出边中随机选择 2 条
gremlin> g.V().outE().sample(2);
==>e[15][2-brother->5]
==>e[18][5-brother->2]
# 从所顶点的 name 属性中随机选取 3 个
gremlin> g.V().values('name').sample(3);
==>hercules
==>sea
==>jupiter
# 从所有的 character 中根据 age 随机选择 3 个
gremlin> g.V().hasLabel('character').sample(3).by('age');
==>v[1]
==>v[2]
==>v[6]
# 与 local 联合使用做随机漫游
# 从顶点 pluto 出发做 3 次随机漫游
gremlin> g.V(pluto).repeat(local(bothE().sample(1).otherV())).times(3).path();
==>[v[8],e[26][8-brother->5],v[5],e[18][5-brother->2],v[2],e[13][2-father->1],v[1]]
# 每个顶点按 0.5 的概率过滤
gremlin> g.V().coin(0.5);
==>v[1]
==>v[2]
...
# 输出所有 location 类顶点的 name 属性,否则输出 not a location
gremlin> g.V().choose(hasLabel('location'), values('name'), constant('not a location'));
==>not a location
==>not a location
==>sky
...
结果存取口袋 SackGraph
包含本地数据结构的遍历器称为口袋。sack() 将数据放入口袋,或者从口袋取出数据。每个遍历器的每个口袋都是通过 withSack() 创建的。
# 创建一个包含常数 1 的口袋,并且在最终取出口袋中的值
gremlin> g.withSack(1).V().sack();
==>1
==>1
...
遍历栅栏 barrierGraph
barrier() 在某个位置插入一个栅栏,以强制该位置之前的步骤必须都执行完成才可以继续往后执行。
# 利用隐式 barrier 计算特征向量中心性
# 包括 groupCount、cap,按照降序排序
gremlin> g.V().repeat(both().groupCount('m')).times(5).cap('m').order(local).by(values, decr);
局部操作 localGraph
通过 Gremlin 进行图遍历通常是当前 step 处理前一 step 传递过来的对象流。很多操作是针对传递过来的对象流中的全部对象进行操作,但也有很多时候需要针对对象流中的单个对象而非对象流中的全部对象进行操作。这种对单个对象的局部操作,可以使用 local() 语句实现。
# 不使用 local()
gremlin> g.V().hasLabel('character').as('character').properties('age').order().by(value,decr).limit(2).value().as('age').select('character', 'age').by('name').by();
==>[character:saturn,age:10000]
==>[character:jupiter,age:5000]
# 使用 local()
gremlin> g.V().hasLabel('character').as('character').local(properties('age').order().by(value).limit(2)).value().as('age').select('character', 'age').by('name').by()
==>[character:saturn,age:10000]
==>[character:jupiter,age:5000]
==>[character:neptune,age:4500]
==>[character:hercules,age:30]
...
# 查询 monster 的属性 map
gremlin> g.V()hasLabel('character').has('type', 'type').propertyMap();
==>[name:[vp[name->nemean]],type:[vp[type->monster]],age:[vp[age->20]]]
==>[name:[vp[name->hydra]],type:[vp[type->monster]],age:[vp[age->0]]]
==>[name:[vp[name->cerberus]],type:[vp[type->monster]],age:[vp[age->0]]]
# 查询 monster 的属性个数
gremlin> g.V()hasLabel('character').has('type', 'monster').propertyMap().count(local);
==>3
==>3
==>3
# 数目最多的顶点类型的顶点数目
gremlin> g.V().groupCount().by(label).select(values).max(local);
==>9
# 所有顶点的属性列表中的第一个属性
gremlin> g.V().valueMap().limit(local, 1);
==>[name:[saturn]]
==>[name:[jupiter]]
==>[name:[sky]]
...
# 不加 local
gremlin> g.V().valueMap().limit(1);
==>[name:[saturn],type:[titan],age:[10000]]
# 所有顶点作为一个集合,从中采样 2 个
gremlin> g.V().fold().sample(local,2);
==>[v[8],v[1]]
执行统计和分析Graph
Gremlin 提供两种语句对执行的查询语句进行统计和分析:
explain(),详细描述原始的 Gremlin 语句在编译期是如何转变为最终要执行的 step 集合的profile(),统计 Gremlin 语句执行过程中的每个 step 消耗的时间和通过的对象等统计信息
# explain()
gremlin> g.V().hasLabel('character').explain();
==>Traversal Explanation
==========================================================================================
Original Traversal [GraphStep(vertex,[]), HasStep([~label.eq(character)])]
ConnectiveStrategy [D] [GraphStep(vertex,[]), HasStep([~label.eq(character)])]
MatchPredicateStrategy [O] [GraphStep(vertex,[]), HasStep([~label.eq(character)])]
...
StandardVerificationStrategy [V] [TinkerGraphStep(vertex,[~label.eq(character)])]
Final Traversal [TinkerGraphStep(vertex,[~label.eq(character)])]
# profile()
gremlin> g.V().out('father').profile()
==>Traversal Metrics
Step Count Traversers Time (ms) % Dur
=============================================================================================================
TinkerGraphStep(vertex,[]) 12 12 0.644 45.66
VertexStep(OUT,[father],vertex) 2 2 0.534 37.83
NoOpBarrierStep(2500) 2 2 0.233 16.51
>TOTAL - - 1.411 -