自定义 sink (NebulaSink)Graph
Nebula Flink Connector 支持以 DataStream.addSink 的方式将 Flink 数据流写入 NebulaGraph 数据库。
说明:Nebula Flink Connector 使用 Flink 1.11-SNAPSHOT 开发,这个版本已经不再支持使用
writeUsingOutputFormat方式定义输出端的接口,源码如下。所以,在使用自定义 NebulaSink 时,请您务必使用DataStream.addSink方式。/** @deprecated */ @Deprecated @PublicEvolving public DataStreamSink<T> writeUsingOutputFormat(OutputFormat<T> format) { return this.addSink(new OutputFormatSinkFunction(format)); }
Nebula Flink Connector 中实现了自定义的 NebulaSinkFunction,开发者通过调用 dataSource.addSink 方法并将 NebulaSinkFunction 对象作为参数传入即可实现将 Flink 数据流写入 NebulaGraph 数据库中。
NebulaSink 的实现类图如下所示。
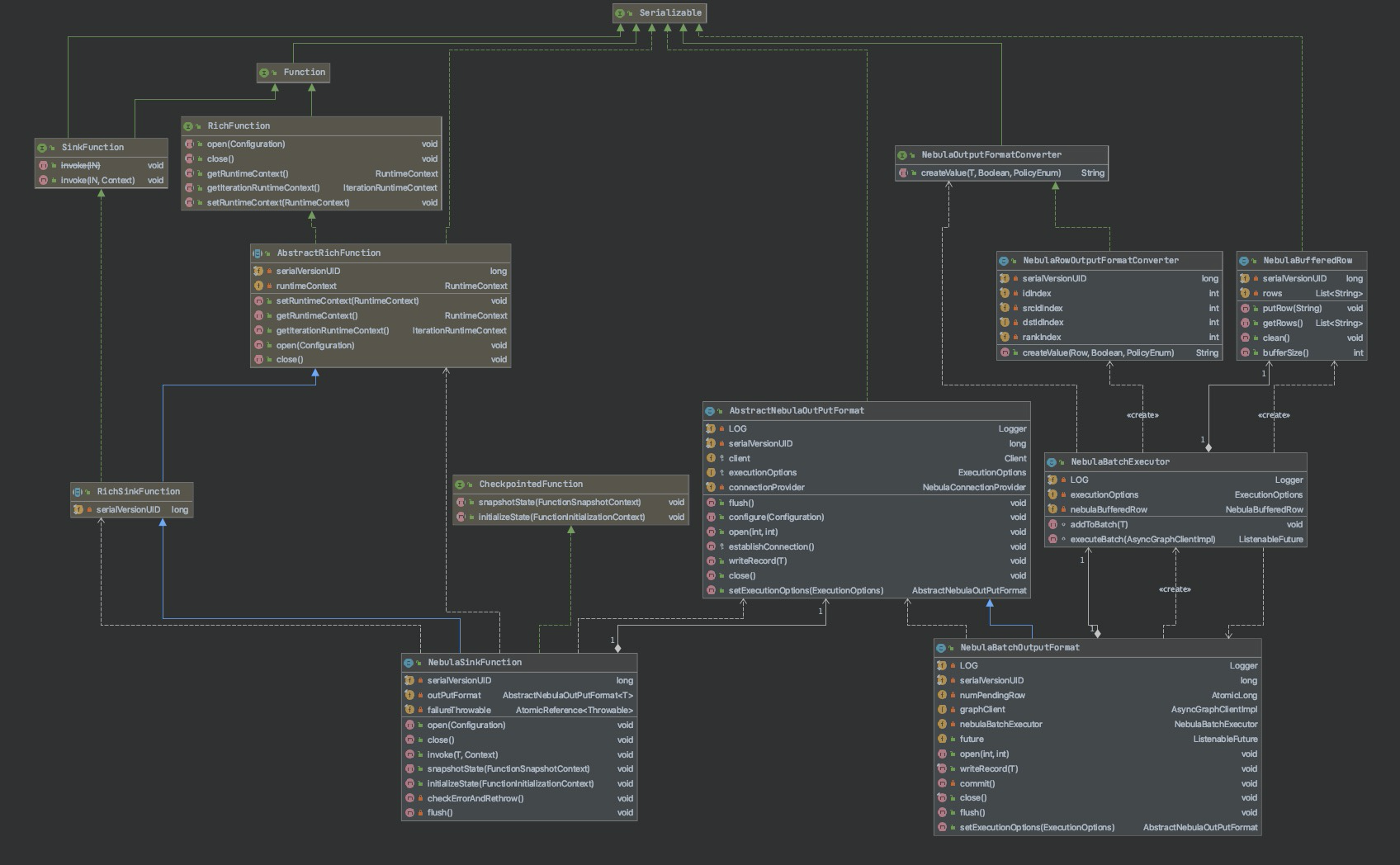
最重要的两个类是 NebulaSinkFunction NebulaBatchOutputFormat。
NebulaSinkFunctionGraph
NebulaSinkFunction 继承自 AbstractRichFunction 并实现了以下方法:
open:调用NebulaBatchOutputFormat的open方法以准备资源。close:调用NebulaBatchOutputFormat的close方法以释放资源。invoke:是 NebulaSink 中的核心方法,调用NebulaBatchOutputFormat中的write方法写入数据。flush:调用NebulaBatchOutputFormat的flush方法提交数据。
NebulaBatchOutputFormatGraph
NebulaBatchOutputFormat 继承自 AbstractNebulaOutPutFormat,而后者继承自 RichOutputFormat,主要实现了以下方法:
open:准备 NebulaGraph 数据库的 Graph 服务的连接,并初始化数据写入执行器nebulaBatchExecutor。close:提交最后批次的数据,等待最后提交的回调结果并关闭服务连接等资源。writeRecord:核心方法,将数据写入 bufferedRow 中,并在达到配置的批量写入上限时提交写入。NebulaSink 的写入操作是异步的,所以需要执行回调来获取执行结果。flush:当 bufferedRow 存在数据时,将数据提交到 NebulaGraph 中。
在 AbstractNebulaOutputFormat 中调用了 NebulaBatchExecutor,用于数据的批量管理和批量提交,并通过定义回调函数接收批量提交的结果,代码如下:
/**
* write one record to buffer
*/
@Override
public final synchronized void writeRecord(T row) throws IOException {
nebulaBatchExecutor.addToBatch(row);
if (numPendingRow.incrementAndGet() >= executionOptions.getBatch()) {
commit();
}
}
/**
* put record into buffer
*
* @param record represent vertex or edge
*/
void addToBatch(T record) {
boolean isVertex = executionOptions.getDataType().isVertex();
NebulaOutputFormatConverter converter;
if (isVertex) {
converter = new NebulaRowVertexOutputFormatConverter((VertexExecutionOptions) executionOptions);
} else {
converter = new NebulaRowEdgeOutputFormatConverter((EdgeExecutionOptions) executionOptions);
}
String value = converter.createValue(record, executionOptions.getPolicy());
if (value == null) {
return;
}
nebulaBufferedRow.putRow(value);
}
/**
* commit batch insert statements
*/
private synchronized void commit() throws IOException {
graphClient.switchSpace(executionOptions.getGraphSpace());
future = nebulaBatchExecutor.executeBatch(graphClient);
// clear waiting rows
numPendingRow.compareAndSet(executionOptions.getBatch(),0);
}
/**
* execute the insert statement
*
* @param client Asynchronous graph client
*/
ListenableFuture executeBatch(AsyncGraphClientImpl client) {
String propNames = String.join(NebulaConstant.COMMA, executionOptions.getFields());
String values = String.join(NebulaConstant.COMMA, nebulaBufferedRow.getRows());
// construct insert statement
String exec = String.format(NebulaConstant.BATCH_INSERT_TEMPLATE, executionOptions.getDataType(), executionOptions.getLabel(), propNames, values);
// execute insert statement
ListenableFuture<Optional<Integer>> execResult = client.execute(exec);
// define callback function
Futures.addCallback(execResult, new FutureCallback<Optional<Integer>>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(Optional<Integer> integerOptional) {
if (integerOptional.isPresent()) {
if (integerOptional.get() == ErrorCode.SUCCEEDED) {
LOG.info("batch insert Succeed");
} else {
LOG.error(String.format("batch insert Error: %d",
integerOptional.get()));
}
} else {
LOG.error("batch insert Error");
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable throwable) {
LOG.error("batch insert Error");
}
});
nebulaBufferedRow.clean();
return execResult;
}
由于 NebulaSink 的写入是批量、异步的,所以在最后业务结束关闭(close)资源之前需要将缓存中的批量数据提交且等待写入操作的完成,以防在写入提交之前提前关闭 NebulaGraph 的客户端,代码如下:
/**
* commit the batch write operator before release connection
*/
@Override
public final synchronized void close() throws IOException {
if(numPendingRow.get() > 0){
commit();
}
while(!future.isDone()){
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
LOG.error("sleep interrupted, ", e);
}
}
super.close();
}
应用实践Graph
Flink 将处理完成的数据 sink 到 NebulaGraph 数据库时,需要将 Flink 数据流进行 map 转换成 NebulaSink 可接收的数据格式。自定义 NebulaSink 的使用方式是通过 addSink 的形式,
您可以按以下步骤使用 Nebula Flink Connector 的 NebulaSink 向 NebulaGraph 写入数据:
- 将 Flink 数据转换成 NebulaSink 可以接受的数据格式。
- 将
NebulaSinkFunction作为参数传给addSink方法来实现 Flink 数据流的写入。
在构造的 NebulaSinkFunction 中分别对客户端参数和执行参数作了如下配置:
NebulaClientOptions需要配置:- NebulaGraph 图数据库 Graph 服务的 IP 地址及端口号。如果有多个地址,使用英文逗号分隔。
- NebulaGraph 图数据库的账号及其密码。
VertexExecutionOptions需要配置:- 需要写入点数据的 NebulaGraph 图数据库中的图空间名称。
- 需要写入的标签(点类型)名称。
- 需要写入的标签属性。
- 需要写入的点 VID 所在 Flink 数据流 Row 中的索引。
- 单次写入 NebulaGraph 的数据量限值,默认为 2000。
EdgeExecutionOptions需要配置:- 需要写入边数据的 NebulaGraph 图数据库中的图空间名称。
- 需要写入的边类型。
- 需要写入的边类型属性。
- 需要写入的边起点 VID(src_Id)所在 Flink 数据流 Row 中的索引。
- 需要写入的边终点 VID(dst_Id)所在 Flink 数据流 Row 中的索引。
- 需要写入的边 rank 所在 Flink 数据流 Row 中的索引。如果不配置,则写入边数据时不带 rank 信息。
- 单次写入的数据量限值,默认值为 2000。
假设需要写入点数据的 NebulaGraph 图数据库信息如下:
- Graph 服务为本地单副本部署,使用默认端口
- 图空间名称:
flinkSink - 标签:
player - 标签属性:
name和age
以下为自定义 NebulaSink 的代码示例。
// 构造 NebulaGraph 的 Graph 服务客户端连接需要的参数
NebulaClientOptions nebulaClientOptions = new NebulaClientOptions
.NebulaClientOptionsBuilder()
.setAddress("127.0.0.1:3699")
.build();
NebulaConnectionProvider graphConnectionProvider = new NebulaGraphConnectionProvider(nebulaClientOptions);
// 构造 NebulaGraph 写入点数据的操作参数
List<String> cols = Arrays.asList("name", "age")
ExecutionOptions sinkExecutionOptions = new VertexExecutionOptions.ExecutionOptionBuilder()
.setGraphSpace("flinkSink")
.setTag(tag)
.setFields(cols)
.setIdIndex(0)
.setBatch(2)
.builder();
// 将点数据写入 NebulaGraph
dataSource.addSink(nebulaSinkFunction);
NebulaSink 示例程序Graph
您可以参考 GitHub 上的示例程序 Graph 编写您自己的 Flink 应用程序。
以 testSourceSink 为例:该程序以 NebulaGraph 的图空间 flinkSource 作为 source,通过 Flink 读取进行 map 类型转换后的数据,再写入 NebulaGraph 另一个图空间 flinkSink,即 NebulaGraph 一个图空间 flinkSource 的数据流入另一个图空间 flinkSink 中。